The complete vegetarian diet, a plant-based nutritional approach, has gained significant popularity for its ethical, environmental, and health benefits. Embarking on a vegetarian journey involves eliminating all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy, offering a unique perspective on mindful eating.
Beyond its ethical stance against animal consumption, vegetarianism promotes environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with animal agriculture. Moreover, it offers numerous health advantages, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved blood pressure, and lower obesity rates.
Introduction
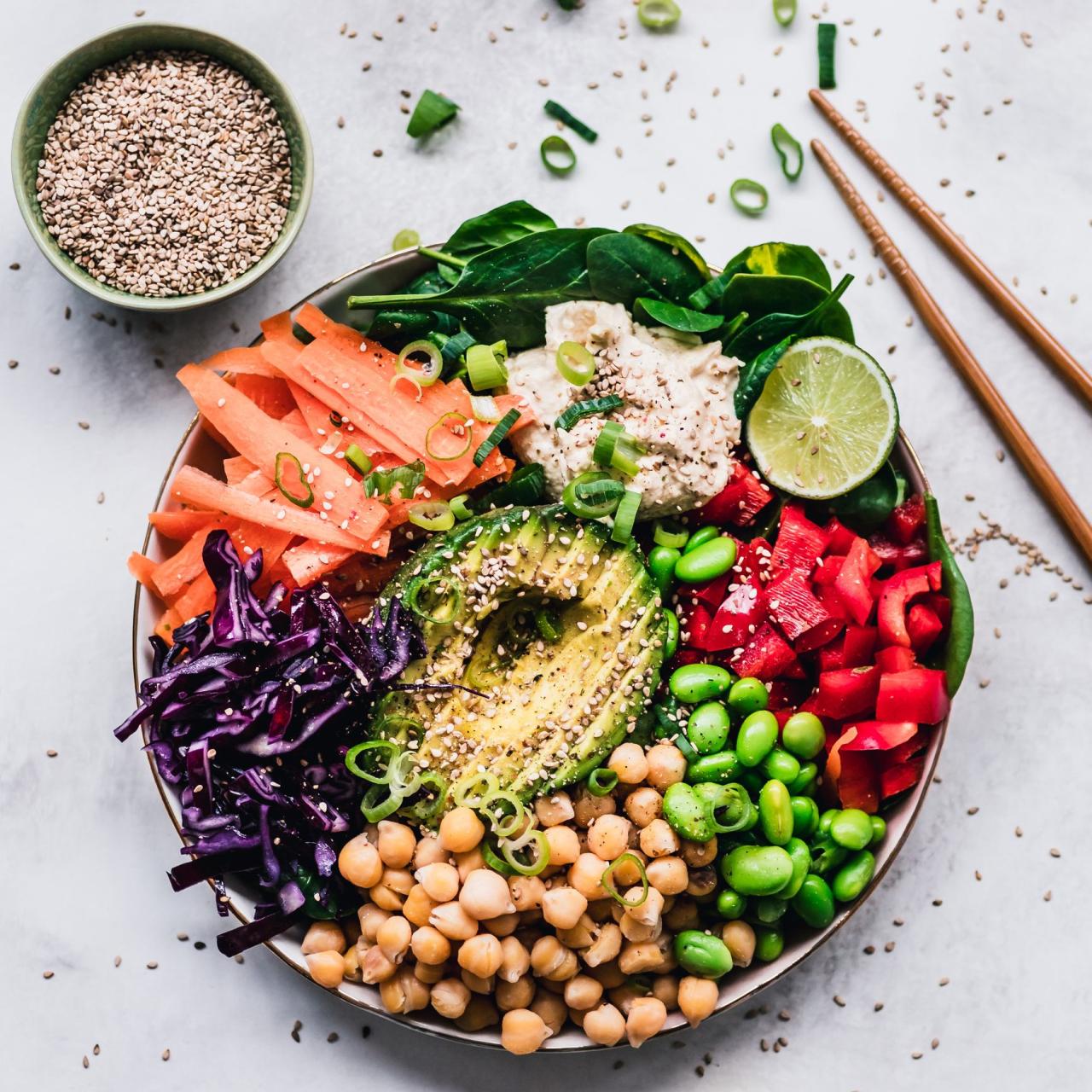

A complete vegetarian diet excludes all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, seafood, eggs, and dairy products. This diet emphasizes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Individuals adopt a complete vegetarian diet for various reasons, including ethical concerns about animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and health benefits.
Ethical Reasons
- Animal Welfare:Vegetarians believe that animals should not be subjected to suffering or exploitation for food.
- Environmental Sustainability:Animal agriculture contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. A vegetarian diet reduces these impacts.
Health Benefits
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:A vegetarian diet is associated with a lower risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
- Improved Nutrient Intake:Vegetarian diets provide abundant fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health.
- Weight Management:Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories and fat than animal products, which can aid in weight loss and maintenance.
Types of Complete Vegetarian Diets
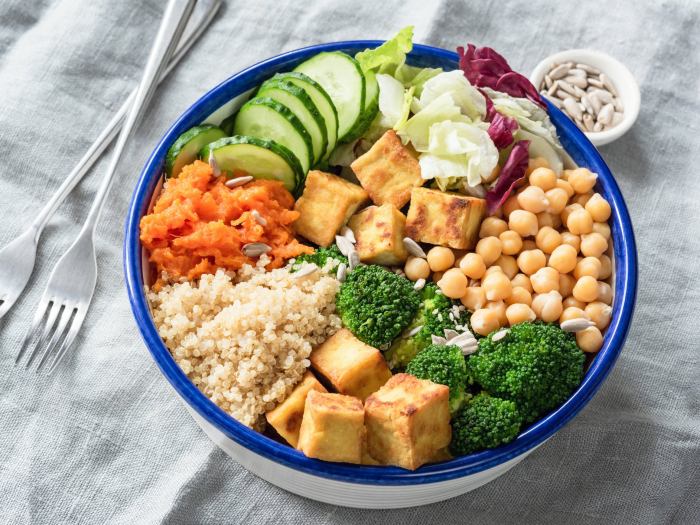

Complete vegetarian diets are those that exclude all meat, fish, and poultry. There are several types of complete vegetarian diets, each with its own set of restrictions and benefits.
The main types of complete vegetarian diets are:
Lacto-vegetarian diet, Complete vegetarian diet
Lacto-vegetarians eat dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, but they do not eat eggs or meat.
Lacto-ovo vegetarian diet
Lacto-ovo vegetarians eat dairy products and eggs, but they do not eat meat.
Ovo-vegetarian diet
Ovo-vegetarians eat eggs, but they do not eat dairy products or meat.
Vegan diet
Vegans do not eat any animal products, including dairy products, eggs, or meat.
Vegetarians are often faced with the question of whether or not they can eat seafood. The answer to this question is not always clear-cut, as there are different types of vegetarian diets and different opinions on what constitutes seafood. However, one thing that is clear is that pescatarians, who eat fish and other seafood but no other meat, are not considered vegetarians.
If you’re wondering can vegetarians eat seafood , the answer is no, not according to the traditional definition of vegetarianism.
Benefits of a Complete Vegetarian Diet
A complete vegetarian diet offers a wide range of health benefits, contributing to overall well-being and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
One of the most significant advantages is the reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer. Vegetarian diets are typically high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and other protective compounds that help combat inflammation and oxidative stress.
Improved Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels
Complete vegetarian diets are often associated with lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. The high fiber content in plant-based foods helps lower cholesterol by binding to it in the digestive tract and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. Additionally, vegetarian diets tend to be lower in saturated fat and cholesterol, which further contributes to improved cardiovascular health.
Lower Risk of Obesity
Vegetarian diets are generally lower in calories and higher in fiber compared to non-vegetarian diets. Fiber promotes satiety and fullness, leading to reduced calorie intake and weight management. Studies have shown that vegetarians have a lower risk of obesity and are less likely to gain weight over time.
Increased Intake of Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains
Complete vegetarian diets emphasize the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, which are essential for optimal health. By adopting a vegetarian diet, individuals can significantly increase their intake of these nutrient-rich foods.
Planning a Complete Vegetarian Diet
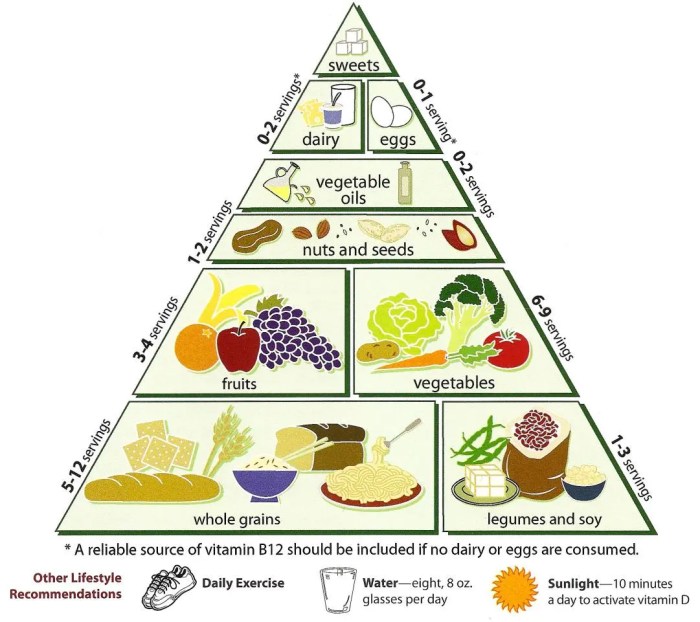
Planning a complete vegetarian diet requires careful consideration to ensure you meet all your nutritional needs. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you create a balanced and healthy meal plan:
Create a Meal Plan
Include a variety of foods from all food groups in your meal plan. Aim for a balance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats.
Protein Sources
Vegetarian diets can provide ample protein. Include protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa in your meals. Combine different plant-based proteins throughout the day to ensure you’re getting all the essential amino acids.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is not naturally found in plant foods. Fortify foods like plant-based milk, cereals, and nutritional yeast with vitamin B12, or take a supplement to ensure adequate intake.
Calcium
Leafy green vegetables, fortified plant milks, and tofu are excellent sources of calcium. Aim to include these foods in your daily diet to meet your calcium needs.
Iron
Iron is essential for red blood cell production. Beans, lentils, and spinach are rich in iron. Enhance iron absorption by pairing these foods with vitamin C-rich fruits or vegetables.
Vegetarians abstain from consuming meat, but what about seafood? The answer is a bit complicated. Some vegetarians choose to include seafood in their diet, while others avoid it. Can vegetarians eat seafood ? The answer depends on the individual’s definition of vegetarianism.
Conclusion
A complete vegetarian diet offers numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved weight management, and enhanced nutrient intake. However, it also poses challenges such as ensuring adequate protein, vitamin B12, and iron intake.
To plan and follow a complete vegetarian diet successfully, consider the following tips:
Meal Planning
- Include a variety of plant-based protein sources, such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and nuts.
- Fortify foods with vitamin B12, or consider supplementation.
- Consume iron-rich foods, such as leafy green vegetables, fortified cereals, and legumes.
- Balance meals with whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to ensure adequate fiber and nutrient intake.
Lifestyle Habits
- Read food labels carefully to identify hidden animal products.
- Inform restaurants and social gatherings about dietary preferences to avoid accidental consumption of meat or animal products.
- Seek support from a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalized guidance and monitoring.
Adopting a complete vegetarian diet requires careful planning and attention to nutritional needs. By following these tips and seeking professional advice when necessary, individuals can reap the benefits of this plant-based lifestyle while mitigating potential challenges.
Ultimate Conclusion
While adopting a complete vegetarian diet presents challenges such as ensuring adequate protein and vitamin B12 intake, careful planning and supplementation can address these concerns. Embracing this plant-based lifestyle not only aligns with ethical and environmental values but also promotes overall well-being and longevity.
Popular Questions
What are the different types of complete vegetarian diets?
There are several types of complete vegetarian diets, including lacto-vegetarian (consumes dairy), lacto-ovo vegetarian (consumes dairy and eggs), ovo-vegetarian (consumes eggs), and vegan (excludes all animal products).
How can I ensure I’m getting enough protein on a vegetarian diet?
Plant-based protein sources include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds. Combining these foods throughout the day can help meet protein requirements.
Is it difficult to get enough vitamin B12 on a vegetarian diet?
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products, so vegetarians may need to consume fortified foods or take supplements to ensure adequate intake.